Categories
Notifications can be categorized into groups, allowing you to control how the system displays them. Categories also provide the ability to display Quick Actions.
Before assigning a notification to a category, it must first be created.
At minimum, a category must be created with a unique identifier using the setNotificationCategories
method, one of more categories will be set on the device. All categories must be set at once with this method as it
overrides any pre-existing categories on the device.
import notifee from '@notifee/react-native';
async function setCategories() {
await notifee.setNotificationCategories([
{
id: 'post',
actions: [
{
id: 'like',
title: 'Like Post',
},
{
id: 'dislike',
title: 'Dislike Post',
},
],
},
]);
}
To view more about the actions property, view the Quick Actions
documentation.
It is also possible to group notifications via threadId.
Assigning a category
Once created, a notification can then be displayed using the categoryId identifier on the notification. For example,
using the post category:
import notifee from '@notifee/react-native';
notifee.displayNotification({
title: 'New post from John',
body: 'Hey everyone! Check out my new blog post on my website.',
ios: {
categoryId: 'post',
},
});
When displayed, the notification will be assigned to the category, and will contain the actions:
Category summary text
After a number of unread notifications have been delivered to the device, iOS will begin to stack notifications for your application. The notification on the top of the stack by default will display summary text, letting the user know how many unread notifications are available:
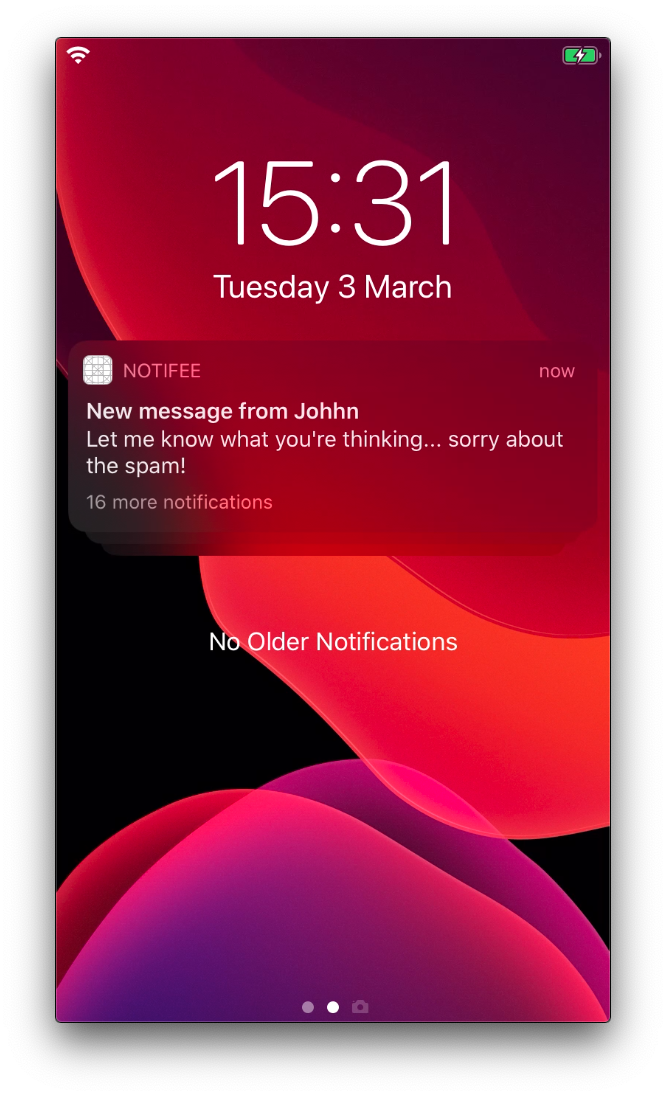
This functionality is only available on iOS >= 12.
If required, you can override the default summary text using the summaryFormat property. This string accepts two unique
values which the system replaces with variable arguments:
%u: the notification count (the system handles this automatically).%@: a custom argument provided to the notification body (see below).
These unique values can be placed inside of the summaryFormat field, and controlled via the summaryArgument and
summaryArgumentCount properties on the notification body, for example:
import notifee from '@notifee/react-native';
await notifee.setNotificationCategories([
{
id: 'post',
summaryFormat: 'You have %u+ unread messages from %@.',
actions: [
{
id: 'reply',
title: 'Reply',
},
],
},
]);
notifee.displayNotification({
title: 'New post from John',
body: 'Hey everyone! Check out my new blog post on my website.',
ios: {
categoryId: 'post',
summaryArgument: 'John',
summaryArgumentCount: 10,
},
});
Category Actions
To learn more about creating actions, view the Quick Actions documentation.
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License and code samples are licensed under the Apache 2.0 License.
All product names, logos, and brands are property of their respective owners. All company, product and service names used in this website are for identification purposes only. Use of these names, logos, and brands does not imply endorsement.